2024-05-06
Inclusive growth is an economic and social concept that emphasizes the equitable distribution of benefits from economic growth across all segments of society. It seeks to ensure that the benefits of development are shared by a wide range of people, rather than being concentrated in the hands of a few , both in monetary and non-monetary terms.
SALIENT FEATURES OF INCLUSIVE GROWTH
- Focus on reducing poverty
- Inclusive growth aims to reduce poverty and inequality by ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are distributed more equitably across society.
- Promotion of employment
- It focuses on creating more and better job opportunities, particularly for vulnerable groups such as women, youth, and people with disabilities.
- Investment in human capital
- It recognizes the importance of investing in education, health, and other social services to improve the capabilities and well-being of individuals and communities.
- Protection of natural resources
- It acknowledges the importance of protecting natural resources and the environment, to ensure that future generations can also benefit from economic growth.
- Encouragement of innovation
- Inclusive growth promotes innovation and entrepreneurship, to create new and more sustainable sources of economic growth and to provide opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Support for marginalized groups
- Inclusive growth recognizes the importance of supporting marginalized groups such as women, indigenous peoples, and ethnic minorities, to ensure that they are not left behind in the economic development process.
- Emphasis on social inclusion
- Inclusive growth emphasizes social inclusion and the reduction of social exclusion, discrimination, and inequalities in access to services and opportunities.
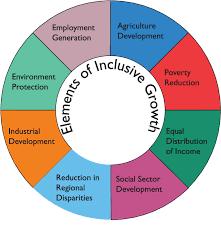
ELEMENTS OF INCLUSIVE GROWTH
1. Skill Development
- Harnessing the demographic dividend will depend upon the employability of the working age population, their health, education, vocational training and skills. Skill development plays a key role here. India is facing a dual challenge in skill development.
- Financial Inclusion
- Financial Inclusion is the process of ensuring access to financial services to vulnerable groups at affordable costs.
- Financial inclusion is necessary for inclusive growth as it leads to the culture of saving, which initiates a virtuous cycle of economic development
- Technological Advancement
- The world is moving towards an era of Industrial Revolution 4.0. These technological advancements have capabilities to both decrease or increase the inequality depending on the way these are being used.
- Social Development
- It means the empowerment of all marginalised sections of the population like SC/ST/OBC/Minorities, women and transgenders.
- Empowerment can be done by improving institutions of the social structure i.e. hospitals especially primary care in the rural areas, schools, universities, etc.
- Investment in social structures will not only boost financial growth but will also create a healthy and capable generation to handle future work.
SIGNIFICANCE OF INCLUSIVE GROWTH
1. Reduction of Poverty and Inequality
- Inclusive growth aims to reduce poverty and income inequality by providing opportunities and benefits to marginalized and vulnerable groups.
- Social Stability
- It contributes to social stability by addressing disparities that can lead to social unrest and conflicts.
- Economic Sustainability
- Inclusive growth promotes long-term economic sustainability by fostering human capital development, increasing productivity, and enhancing overall economic resilience.
- Improved Well-being
- It enhances the well-being and living standards of a larger portion of the population, leading to a higher quality of life for many.
NECESSITY OF INCLUSIVE GROWTH
1. Social Equity
- It promotes social justice by ensuring that economic opportunities are accessible to all, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Economic Stability
- Reducing inequality can contribute to economic stability by preventing extreme disparities in wealth and income.
- Human Capital Development
- It fosters human capital development through improved access to education, healthcare, and skills training.
- Political Stability
- Addressing economic disparities can help prevent political instability and conflicts that may arise from social grievances
CHALLENGES IN ACHIEVING INCLUSIVE GROWTH
- Unequal distribution of resources
- The unequal distribution of resources such as land, water, and other natural resources has led to significant inequality in India.
- Wealth and income are concentrated in the hands of a few, while the majority of the population struggles to make ends meet.
- Gender discrimination
- Women in India face significant discrimination in terms of access to education, employment, and healthcare.
- The prevalence of child marriage and violence against women further exacerbate gender inequality.
- Regional disparities
- There are significant regional disparities in India, with some areas of the country being much more developed and prosperous than others.
- This leads to unequal opportunities for people in different parts of the country.
- Corruption and inefficiency
- Corruption and inefficiency in government institutions and public services perpetuate inequality in India.
- This affects access to basic services such as healthcare and education, particularly for those who are marginalized or disadvantaged.
- Lack of social protection
- The absence of effective social protection systems, such as social security, healthcare, and unemployment benefits, further exacerbates inequality in India, particularly for those who are poor and vulnerable.
- Social and cultural obstacles
- Marginalised groups may encounter social and cultural obstacles that restrict them from accessing opportunities and services, such as discrimination, exclusion, and gender inequity.
- Political unrest
- Political unrest can impede economic expansion and make it challenging to put policies and initiatives that promote equitable growth into place.
- Weak institutional capacity
- Policies and programmes aimed at promoting equitable growth may be less effective if there is a lack of competent workers and insufficient infrastructure, among other factors.
INDIA’S INITIATIVES IN INCLUSIVE GROWTH
- NITI Aayog
- The Indian government’s NITI Aayog is a think tank for policy that supports inclusive and sustainable economic growth.
- Through programmes like the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, it is modernising agriculture.
- Other inclusive growth measures include boosting digital payments and helping start-ups and small and medium-sized businesses flourish.
- Jan Dhan Yojana
- The Jan Dhan Yojana is a financial inclusion programme that was started in 2014 and aims to give all households in the nation access to financial services.
- Through the programme, more than 43 crore bank accounts have been opened as of 2021, boosting financial inclusion and encouraging entrepreneurship.
- Skill India Mission
- It was established in 2015 with the goal of improving young people’s employability by offering them vocational training.
- Over 2.5 billion people have been trained in a variety of skills under the programme, which has also helped to open up work opportunities.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
- It is a housing programme that was started in 2015 and seeks to offer affordable homes to everyone by the year 2022.
- Over 1 crore households have now received houses as a result of the programme.
- Ayushman Bharat
- The 2018-launched Ayushman Bharat scheme intends to give health insurance coverage to more than 10 crore disadvantaged and underprivileged households in the nation, easing the financial burden of healthcare costs.
- MGNREGA
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) is a social welfare programme that was introduced in 2005 and provides every household in rural regions with a 100-day salary employment guarantee.
- Millions of people have received employment possibilities through the programme, which has also helped to reduce poverty.
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- It is a cleanliness initiative that was started in 2014 to encourage sanitation and hygiene, particularly in rural regions.
People’s health and wellbeing, especially those of women and children, have improved as a result of the programme